Fuel Injection System Ppt
INTRODUCTION:: INTRODUCTION: The fuel-injection system is the most vital component in the working of CI engine. The engine performance, power o/p, economy etc is greatly dependent on the effectiveness of the fuel-injection system. Basically the purpose of carburetion & fuel-injection is the same i.e.
Preparation of the combustible charge. But in case of carburetion fuel is atomized by processes relying on the air speed greater than fuel speed at the fuel nozzle, whereas in fuel-injection the fuel speed at the point of delivery is greater than the air speed to atomize the fuel. Requirements of a diesel injection system: Requirements of a diesel injection system The functional requirements of an injection system are listed below; Introduction of the fuel into the combustion chamber should take place within a precisely defined period of the cycle. The metering of amount of fuel injected per cycle should done very accurately.
The quantities of fuel metered should vary to meet the changing load & speed requirements. The injection rate should be such that it results in the desired heat-release pattern. The injected fuel must be broken into very fine droplets. For accomplishing these requirements the following functional elements are required in a fuel injection system;: For accomplishing these requirements the following functional elements are required in a fuel injection system; PUMPING ELEMENT: To move the fuel from the fuel tank to cylinder & piping etc. METERING ELEMENTS: To measure & supply the fuel at the rate demanded by load & speed.
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEMS. Types of Fuel Injection Systems. Port fuel injection. (PFI/MPFI) Throttle Body Fuel Injection. (TBI) Mechanical or CIS injection system.
METERING CONTROL: To adjust the rate of metering elements for changes in load & speed of the engine. DISTRIBUTING ELEMENTS: To divide the metered fuel equally among the cylinder. TIMING CONTROLS: To adjust the start & the stop of injection.
MIXING ELEMENT: To atomizes & distribute the fuel within the combustion chamber. Air injection system: A ir injection system In this method fuel is forced into the cylinder by means of compressed air to a very high pressure. The rate of fuel admission can be controlled by varying the pressure of air. The fuel is metered & pumped to the fuel valve by a camshaft driven fuel pump. The fuel valve is opened by means of a mechanical linkage operated by the camshaft which controls the timing of injection. The fuel valve is also connected to a high pressure air line fed by a multi stage compressor which supplies air at a pressure of about 60 to 70 bar. PowerPoint Presentation: ADVANTAGES; It provides better atomization & distribution of fuel.
Heavy & viscous fuels, which are cheaper can also be injected. DISADVANTAGES; This method is not used now a day due to following reasons: It requires a high pressure multi stage compression. A separate mechanical linkage is required to time the operation of fuel valve. The fuel valve sealing requires considerable skill. Due to the compression & the linkage the bulk of the engine increases.
This also results in reduced B.P due to power loss in operating the compression & linkage. In case of sticking of the fuel valve, the system becomes quite dangerous due to the presence of high pressure air. WORKING OF JERK PUMP INJECTOR:: WORKING OF JERK PUMP INJECTOR: It consists of a reciprocating plunger inside a barrel. The plunger is driven by a camshaft.
The working principle of jerk pump is as follow: Near the port A, fuel is always available under relatively low pressure. While the axial movement of the plunger is through camchaft,its rotational movement is by mean of rack D. Port B is the orifice through which fuel is delivered to the injector.
At this stage it is closed by means of a spring loaded check valve. When the plunger is below port A, the fuel gets filled in the barrel above it. As the plunger rises & closes the port A the fuel will flow out through port C. This is because it has to overcome the spring force of the check valve in order to flow through port B.
Hence it takes the easier way out via port C. PowerPoint Presentation: At this stage rack rotates the plunger & as a result port C also closes. The only escape route for the fuel is pass the check valve through orifice B to the injector. This is the beginning of injection & also the effective stroke of the plunger. The injection continues till the helix on the plunger uncovers port C. Now the fuel will take the easy way out through C & the check valve will close the orifice B. The fuel injection stops & the effective stroke ends.
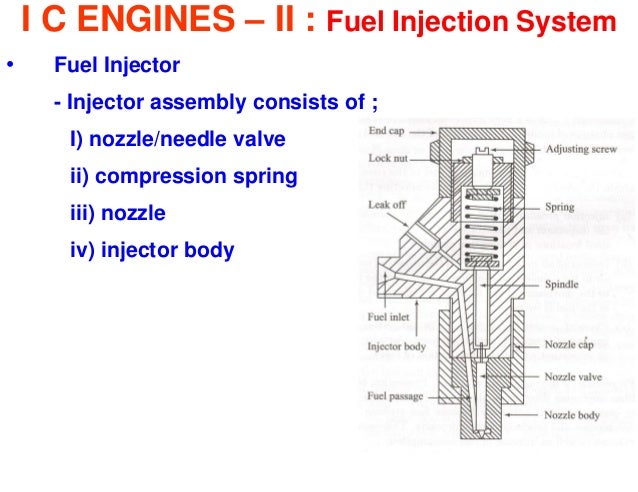
(e) & (f) the plunger is rotated to the position shown. The same sequence of events occur. But in this case port C is uncovered sooner. Hence the effective stroke is shortened. SINGLE HOLE NOZZLE:: SINGLE HOLE NOZZLE: Single hole nozzle are used in open combustion chamber.
At the center of the nozzle body there is a single hole which is closed by the nozzle valve. The size of the hole is usually larger than 0.2mm.
The hole may be drilled centrally or at an angle to the centre line of the nozzle. Main disadvantages of the Single hole nozzle are: Single hole nozzle has tendency to dribble. The spray angle is very narrow.
This does not facilitate good mixing unless higher air velocities are provided. PINTLE NOZZLE:: PINTLE NOZZLE: In order to avoid the weak injection & dribbling the spindle is provided with a projection called pintle, which protrudes through the mouth of the nozzle body. It either cylindrical or conical in shape. The size & shape of the pintle can be varied according to the requirement. Advantages: It is self cleaning type.
It prevent the carbon deposition on the nozzle hole. It result in good atomization. It avoid weak injection & dribbling. Disadvantages: Distribution & penetration poor. Hence not suitable for open combustion chamber. ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM(EFL):: ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM(EFL): Modern gasoline injection system use engine sensors, a computer and solenoid operated fuel injectors to meter & inject the right amount of fuel into the engine cylinder.
These system is called as electronic fuel injection system(EFL) use electrical & electronic devices to monitor & control engine operation. An electronic control unit (ECU) or computer receives electrical signals in the form of current or voltage from various sensors.
It then uses the stored data to operate the injectors, ignition system & other engine related devices. As a result, less unburned fuel leaves the engine as emissions & the vehicle gives better milage. PowerPoint Presentation: Under full load, the ECU will sense a wide open throttle, high intake manifold pressure,& high inlet air flow.
The ECU will then increase the injector pulse width to enrich the mixture which will enable the engine to produce higher power. Under low load & idling conditions, the ECU will shorten the pulse width by which the injectors are kept in the closed position over a longer period of time. Because of this, air-fuel mixture will become leaner & will result in better fuel economy. EFI system has a cold start injector too. This is an extra injector that sprays fuel into the center of the engine intake manifold when the engine is cold. It server the same purpose as the carburetor choke. The cold start injector ensures easy engine start up in very cold weather.
PowerPoint Presentation: Merits of EFI system: Formation of ice on the throttle plate is eliminated. Better atomization & vapourization will make the engine less knock. Manifold wetting is eliminated due to the fuel being injected into or close to cylinder & need not flow through the manifold. Atomization of fuel is independent of cracking speed & therefore starting will be easier. Distribution of fuel being independent of vapourization less volatile fuel can be used.
Position of the injection unit is not so critical & thereby the height of the engine can be less. Demerit of EFI system: High maintenance cost. Difficulty in servicing.
Possibility of malfunction of some sensors. THERMOSYPHON SYSTEM: THERMOSYPHON SYSTEM The basic principle of thermosyphon can be explained with respect to figure. Heat is supplied to the fluid in the tank A.
Fuel Injection System Carburetor
Because of the relatively lower density, the hot fluid travels up, its place being taken up by comparatively cold fluid from the tank B through the pipe p2. The hot fluid flows through the pipe p1 to the tank B where it gets cooled. Thus the fluid circulated through the system in the form of convection currents.
For engine application, tank A represents the cylinder jackets while tank B represents a radiator and water acts the circulating fluid. PowerPoint Presentation: As shown in the figure a cap is fitted on the radiator with two-valves, a safety valve which is loaded by a compression spring and a vacuum valve. When the coolant is cold both the valves are shut, but as the engine warms up the coolant temperature rises until it reaches a certain value corresponding to the desired pressure then the safety valve opens; but if the coolant temperature falls during the engine operation the valve will close again until the temperature again rises to the equivalent pressure value. When the engine is switched off and the coolant cools down vacuum begins to form in the cooling system, but when the internal pressure falls below atmospheric the vacuum valve is opened by the higher outside pressure and the cooling system then attains atmospheric pressure. PowerPoint Presentation: Two types of fins used to cover the cylinder. The length of fins & the spacing b/w them is quite important for efficient cooling. Larger inter-spacing b/w the fins offers larger area for cooling air but the heating of the air is less, so more cooling air is required.
Smaller interspacing b/w the fins results in smaller flow area for cooling air & hence air is heated more & input to the cooling air is less. However, the pressure drop required for flow is more. If the distance b/w two fins is quite small the laminar layer of the opposite area come in contact with each other & the efficiency of the fins is reduced very much. Therefore,a spacing less than 2.5mm is not used. The height of the fins controls the distance b/w the two cylinders and hence, the size of the engine.
Usually the fin height varies from 15 to 25mm. ROLE OF RADIATORS:: ROLE OF RADIATORS: The function of the radiator is to reject coolant heat to the outside air.(by conduction & forced convection & not by radiation) The cooling effect in a radiator is achieved by dispersing the heated coolant into fine stream through the radiator core so that relatively small quantities of coolant are brought in contact with large metal surface areas which in turn are cooled by a stream of air. It should be noted that it is easier o transfer heat from water to the metal surfaces than from metal surface of air. PowerPoint Presentation: The radiator consists of an upper tank (header tank) at the top & a collector tank at the bottom of the radiator core. Two types of radiators in common use are: Down-flow type & cross flow type. In down-flow type,water flow from top to bottom,but in cross flow type the hot coolant is supplied to top of the supply tank, it flows across the radiator and is taken out from the bottom of the collector tank.
A separate header tank is usually provide at the upper end of the collector tank to prevent aeration. ROLE OF THERMOSTATS:: ROLE OF THERMOSTATS: Too low a cylinder barrel temperature, may result in severe corrosion damage due to condensation of acids on barrel walls. To avoid such a situation it is customary to use a thermostat to stop flow of coolant below preset cylinder barrel temp. Most modern cooling system embody a thermostatic device which prevents the water in the engine jacket from circulating through the radiate for cooling until its temp has reached to valve suitable for efficient engine operation. The thermostat bypass valve is filled b/w engine & the radiator top. The thermostat valve is operated by a small elements filled with wax.
As the temp increases, the wax melts and valve is opened to allow coolant to go to the radiator. Under normal operating temp the valve remains open. When the temp falls,the valve is closed bypassing the water and thus, cooling is automatically ceased. QUESTIONS;: QUESTIONS; What are the functional elements required for accomplishing the objectives of diesel engine fuel injection system? Also mention the location of these elements with the help of symbolic representation explain i ) Individual pump and injector type.ii) Common rail type. Explain the following with simple sketches i ) Thermostat ii) Radiator Discuss five important requirements of an ideal diesel injection system. Draw a sketch of Pintaux nozzle and discuss its merits.
How are injection systems Classified? Describe them briefly. What are the limitations of air injection system? With a neat sketch explain the Jerk pump injection system. With a neat sketch explain: i ) Forced circulation-cooling system.
Ii) Evaporative cooling system. Describe with suitable sketches common rail system and distributor injection. What is the function of a radiator? Explain the construction of a typical radiator system of fuel.
Ppt of fuel injection system. 1. Prepared By: Upadhyay Ayush. (53) GANDHINAGAR INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ACTIVE LEARNING ASSIGNMENT ON “Type of Injection System” INTERNAL COMBUTION ENGINE2161902 MECHANICAL 6 (D3) GUIDED BY:- Prof. HARDIK GOHEL.
Introduction Fuel-Injection System is vital to the working and performance of CI engine. This system serves the purpose of initiating and controlling the combustion to meet the demand requirements. Fuel is injected into combustion chamber towards the end of compression.
It is atomized as it enters under high velocity and the droplets get vaporized to form a fuel-air mixture. Due to continued heat transfer from hot air to fuel, the fuel reaches to its self ignition temperature to ignite spontaneously initiating combustion. Depending upon the demand requirements the fuel injection system continues to deliver the fuel during initial part of combustion. 3/23/2017 I.C.E 2.
Classification 3/23/2017 I.C.E 3 Injection System Air Injection Solid Or Airless Injection Common rail system Individual pump and injector system Distributor system. Air Injection System In this system fuel is injected along wit high pressure air into combustion chamber.
Fuel Injection System Pdf
The pressure of this air is about 70 bar. A multistage air compressor is required to supply the blast of air at high pressures. A fuel pump draws fuel from fuel tank through a filter and discharge a definite quantity into an injector.
The high pressure air from compressor is also led to the injector valve which force the fuel, through the nozzle, when it is opened mechanically. This type of system is not used now-a-days in diesel engines.
3/23/2017 I.C.E 4. 3/23/2017 I.C.E 5 Advantages:- It provides good atomization and distribution of fuel. Fuel pump needs to develop less pressure.
Nagoya University
It requires high pressure multi stage compressor. Air compressor needs extra maintenance.
Disadvantages:-. Solid Injection Or Airless injection system In solid Injection system, fuel is directly injected into the cylinder without aid of compressed air. That’s why this system is called solid or airless injection system. Fuel is supplied at very high pressure (about 200 bar) from fuel pump to fuel injector from where it is injected to the combustion chamber with the help of injector. There are three types as: 1. Common rail system 2. Individual pump and injector 3.
Distributor injection system 3/23/2017 I.C.E 6. Common Rail Injection System In this system, single fuel pump supplies high pressure diesel oil to common rail or header. High pressure in the header forces fuel to each of the nozzle. At given instant, the fuel is injected in a specific cylinder by a mechanically operated valve, by means of a push rod and rocker arm. The amount of fuel is regulated by varying the length of the push rod stroke.
The pressure in header is as per injector design for penetration & dispersion of fuel in combustion chamber. 3/23/2017 I.C.E 7. It can control fuel supply according to load and speed of the engine. Only one pump is required for multi cylinder engine. The arrangement of system is very simple & Maintenance cost is less. 3/23/2017 I.C.E 8 Advantages:- Disadvantages:- Very accurate design and workmanship is required.
Individual Pump & Injector 3/23/2017 I.C.E 9 In this system, individual fuel pump is provided for each nozzle. The metering of fuel quantity and control of injection timing are done by the each pump for corresponding nozzle. The needle valve in nozzle is actuated by fuel oil pressure. The amount of fuel entering the cylinders is regulated by changing position of control rack.
Distributor Injection System In this system, the pump is used to pressurizes, meters and times the injection. Then fuel is supplied to central distributor block.
From distributor block fuel is distributed to each cylinder in correct firing order by cam operated poppet valves which open to admit fuel to nozzles. The amount of fuel to entering the cylinders is regulated by changing position of control rack.
The number of injection strokes per cycle for the pump is equal to the number of cylinders. 3/23/2017 I.C.E 10.